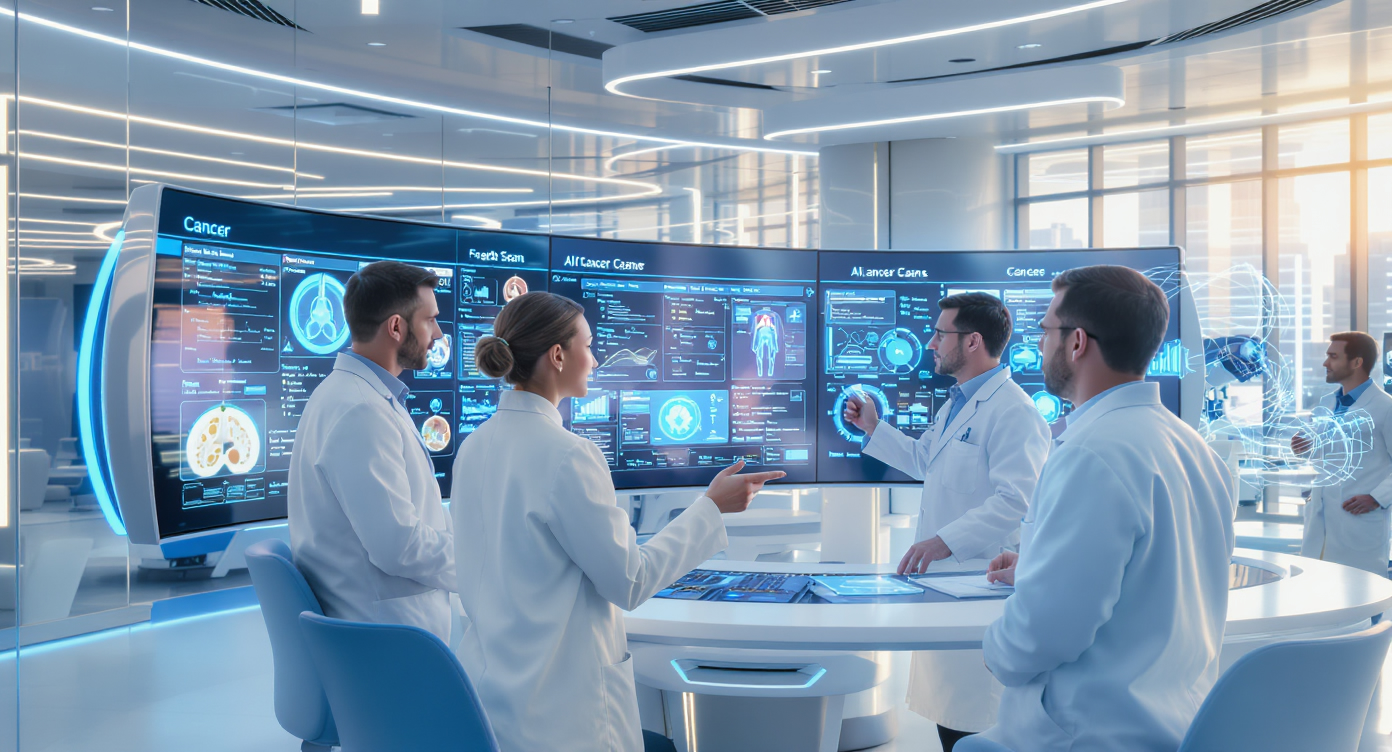
Medical diagnostics is entering a new era. A generative AI system can now analyze blood cells with greater accuracy and confidence than human experts, detecting subtle signs of diseases like leukemia that might escape even experienced pathologists.
How It Works
The AI system examines microscopic images of blood samples, analyzing individual cells for abnormalities. Unlike human experts who might review dozens of cells, the AI can evaluate thousands in seconds, looking for patterns that indicate disease.
The system was trained on millions of blood cell images, learning to recognize the subtle variations in shape, size, color, and texture that distinguish healthy cells from diseased ones. It can identify multiple conditions from a single sample, flagging cases that require immediate attention.
Superior Performance
In clinical trials, the AI demonstrated remarkable capabilities:
Accuracy
The system achieved higher diagnostic accuracy than experienced pathologists, particularly for rare conditions that doctors might only see a few times in their careers.
Consistency
Unlike human experts who may be affected by fatigue or distraction, the AI delivers consistent results whether it’s analyzing the first sample of the day or the thousandth.
Early Detection
The AI detects subtle abnormalities that might be missed in early stages of disease, potentially enabling earlier intervention and better patient outcomes.
Speed
Analysis that might take a pathologist hours can be completed in minutes, accelerating the diagnostic pipeline.
Applications in Healthcare
This technology has immediate applications across medical practice:
Leukemia Detection
Blood cancers like leukemia produce distinctive changes in blood cell populations. The AI can spot these changes earlier and more reliably than traditional methods.
Anemia Diagnosis
Different types of anemia produce different cell abnormalities. The AI can distinguish between them, helping doctors select appropriate treatments.
Infection Identification
Certain infections trigger characteristic changes in white blood cells. The AI can help identify infections faster than traditional culture methods.
Treatment Monitoring
For patients undergoing treatment, the AI can track changes in blood cell populations over time, helping doctors assess whether therapies are working.
The Human-AI Partnership
This technology isn’t designed to replace pathologists—it’s meant to augment them. The AI serves as a highly capable assistant, flagging cases that need attention and providing a second opinion on difficult diagnoses.
Pathologists remain essential for:
- Interpreting results in the context of patient history
- Making final diagnostic decisions
- Handling unusual cases the AI hasn’t been trained on
- Communicating with patients and other doctors
Privacy and Implementation
Healthcare AI raises important questions about privacy and data handling. The systems are designed to process images without storing patient identifiers, and analysis can be performed locally without sending data to external servers.
Implementation is also carefully managed, with hospitals introducing the technology gradually and validating its performance against their own patient populations.
The Future of Medical AI
Blood cell analysis is just one application of AI in healthcare. Similar systems are being developed for radiology, pathology, dermatology, and other specialties where pattern recognition is crucial.
As these tools mature, they promise to democratize access to expert-level diagnostics, bringing sophisticated analysis to underserved areas and helping doctors everywhere provide better care.
The age of AI-assisted medicine is here.
Recommended Reading
Deep Medicine: How AI Can Make Healthcare Human Again
By Eric Topol MD. Explore how AI is transforming medical diagnostics and patient care, making healthcare more accurate and personalized.
As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.
How do you feel about AI playing a larger role in medical diagnostics? Share your thoughts in the comments below.



Comments